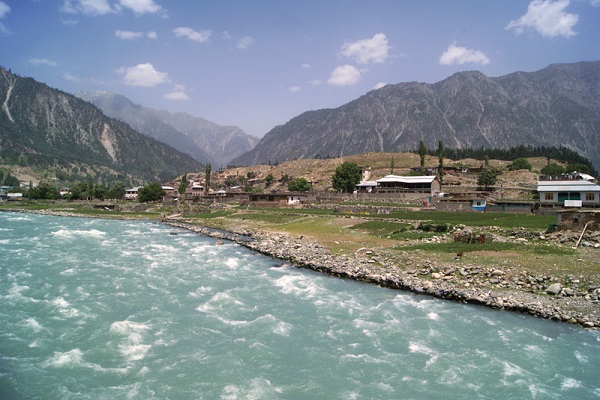
The Swat River is located in the north of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, which comes from the glaciers of Hindu Kush and flows through the valley of Kalaam and joins the River in the region of Swat. The water of the river is a great source of cultivating crops for the nearest regions, and the water is also used for drinking purposes by the people.
There are a number of lakes excavated that provide clear blue water to many areas for the cultivation of crops. The lakes were excavated during British Rule till the year of 1921. Furthermore, it is a beautiful tourist spot where thousands of tourists visit here to see the beauty of the region. This article comprises all the information, including the Swat River Location.
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Information | |
| Location: | Pakistan |
| Type: | River |
| Local Language Name: | د سوات سیند |
| Coordinates : | 34°07′N 71°43′E |
| Website: | https://www.britannica.com/place/Swat-River |
| Location | |
| Countries: | Pakistan |
| Provinces: | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa |
| Cities: | Swat |
| Tributaries | |
| Left: | Ushu Khwar, Bashigram Khwar |
| Right -: | Daral Khwar, Gabral Khwar |
| Source | |
| Location: | Hindu Kush Mountains |
| Mouth | |
| Location: | Charsadda |
| Details | |
| Length: | 240 km (149 mi) |
| Basin: | 14,000 km2 (5,405 sq mi) |
| Discharge average: | 220.5 m3/s |
Table of Contents
Swat River Origin
The word “Swat” is a Sanskrit word that means Blue/ Clearwater. Rigveda referred to River Swat as Suvastu, which means fair dwelling. The word also refers to the settlement of Aryan near the river of Swat. Furthermore, the river is known as Soastus in ancient Greek while China’s Faxian stated it as Su – ho – to.
Swat River Location
The river forms due to the glaciers of the Hindu Kush Mountains, which melt throughout the year and form many small rivers such as Gabral and Osho, which join the River at Swat/Kohistan Valley. After passing Kohistan, it reaches <ydan after a distance of 35 kilometers. Mydan has rocky and sloppy mountains with narrow valleys through which the water of River Swat passes very quickly.
Furthermore, the river flows through Mydan and Chakdara and finally joins the Panjgora River at the place of Qalangi. After Qalangi, the river joins the Valley of Peshawar and finally falls into River Kabul at Charsadda.
Transportation
There are two roads on both sides of the river, starts from Mingora, which is used by the locals and tourists for transportation. The road of the east- bank of the river passes through the regions of Totakan, Bagh Dhera, and Mydan in the south, while on the east of the river’s bank, there is a G T Road.
Both of the roads are connected through many bridges, including the bridges of Bari Kot, Kanju, Chakdara, Totakan, Bagh Dherai, and Khwaza Khel. The road of the western side of the river passes through many valleys, including Khazana, Matta, Nikpi Khel, Sakhoe, and Shawar.
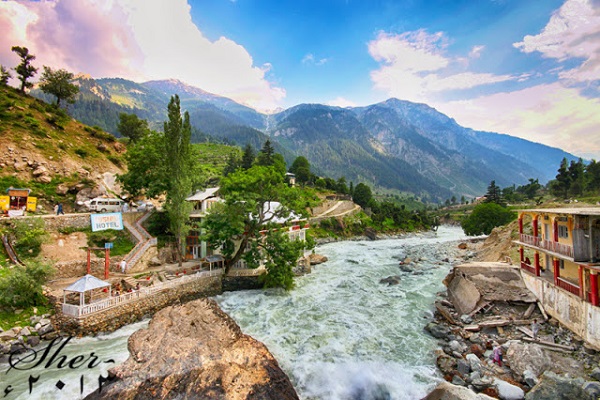

Economical Impact
The river of Swat contributes to the economy of the Swat Valley as there are many canals which are excavated by the British government from 1903 till 1921. These canals provide water to the region of Malakand and Swat. The canal which irrigates the lands of Malakand is regulated by Amandara Head Works.
Furthermore, the canal of Swat was constructed in 1914 during British Rule, which passes through the tunnel of Benton near Malakand Pass. In addition to that, Muda Head Works was built near Dargai in order to regulate a number of canals in the district, which provide water for irrigation to the regions of Mardan, Swabi, and Charsadda. It also boosts springs and Water – Wells through leakage.
Hydro Power
Thousands of Megawatts of electricity are produced by the Hydro – Power Plants installed on the river, which include the following power plants.
- Hydro Power Plant of Jabban – Completed in 1938
- Hydro Power Plant of Dargai – Completed in 1952
Furthermore, before entering the valley of Peshawar, Mohmand Dam is under construction at the end of Swat River near the region of Munda, which will have a capacity of 750 Megawatt of electricity. Other proposed projects for hydropower plant is given below.
- Gabral Hydro Power Plant
- Asrit Kedam Hydro Power Plant
- Matiltan Hydro Power Plant

Swat River Lakes
- Speen Khwar Lake
- Anakar Lake
- Daral Lake
- Izmis Lake
- Maho – dand Lake
- Khaipro Lake
- Bashingtam Lake
- Kandol Lake
Swat River Town/Villages
There are many towns and villages on both sides of the river which are linked through many local roads. Names of some of the villages near the River of Swat are given below:
Western Bank
- Chakdara
- Kabai
- Koza Bandai
- Shamozai
- Ningualai
- Bahrain
- Matta
- Kanju
- Durush Khela
- Kajam
Eastern Bank
- Totakan
- Batkhela
- Khar
- Kota
- Ghalagay
- Barikot
- Balogram
- Manyar
- Odigram
- Thana
- Madyan
- Charbagh
- Qambar
- Manglawar
- Fatehpur

Freshwater Project
In 1999, a feasibility study was undertaken by WWF in order to protect the clean water of Swat River. The study concluded that due to lack of awareness, the water of the river is being polluted which effected the equated life.
An awareness program was conducted in 2000 where the public was introduced with the water pollution including dynamiting, electrocution, and poisoning for the fishing purpose which endangers the water speeches such as fishes.
Many seminars and online programs were held under the project on different social platforms and the awareness was delivered. Many sewerage systems which poisoned the water were blocked and stopped as well as the Water Conservation Act was started functioning.
Social Media Handle
https://www.facebook.com/riversidehotelswat/