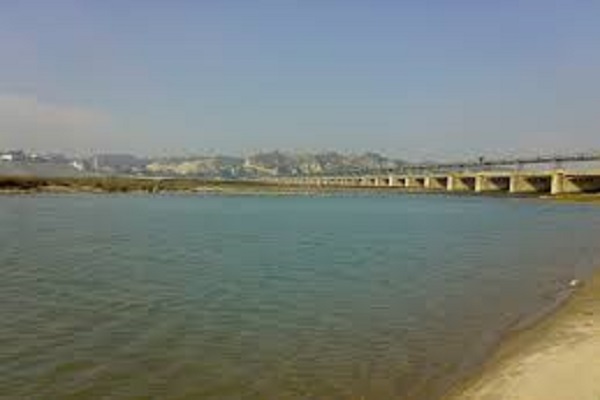
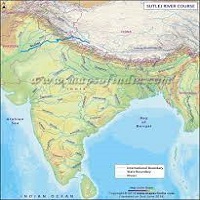
Sutlej River is the longest of all five rivers which pass through India and Pakistan. It is also called Satadree and serves as an Indus River’s tributary. It originates in Tibet from the glaciers of Himalaya and meets the Chenab River in Bahawalpur and then joins the Beas River near Pakistan – India border.
After entering Pakistan, the river flows through Bahawalpur and finally meets the Arabian Sea in Karachi. The water of the river is allocated to India under Indus Water Treaty. Furthermore, there are a number of hydroelectric power plants constructed which provide electric facilities to the people.
Moreover, there are a number of canals on the river that are excavated which provide water to the agricultural lands for better production of the crops. This article summarizes all the information about the river, including Sutlej River History.
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Information | |
| Location: | Between Pakistan and India |
| Type: | Sutlej River |
| Local Language Name: | درياۓ ستلُج |
| Coordinates : | 29°23′23″N 71°3′42″E |
| Location | |
| Countries: | Pakistan and India |
| Provinces: | Punjab |
| Cities: | Bahawalpur |
| Tributaries | |
| Left: | Baspa |
| Right -: | Spiti, Beas |
| Source | |
| Location: | Lake Rakshastal |
| Elevation: | 4,575 m (15,010 ft) |
| Coordinates: | 30°50′39″N 81°12′17″E |
| Mouth | |
| Location: | Bahawalpur district, Punjab, Pakistan |
| Elevation: | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Mouth: | Confluence with Chenab to form the Panjnad River |
| Details | |
| Length: | 1,500 km (932 mi) approx |
| Basin: | 395,000 km2 (152,510 sq mi) approx |
| Discharge : | Ropar |
| Discharge average: | 500 m3/s (17,657 cu ft/s) |
Table of Contents
Sutlej River History
The Sutlej Valley where the water of the river passes was anciently known as Guruda Valley which is situated at a distance of few miles from the Himalayas. The river was also known as the Zaradros River. It was used by the kings and locals of the time as a medium of travel.
It is also used for transportation of goods and wood to the lower side villages of the river including the districts of Hamir – Pur and Bilas – Pur. Different religious books have resembled the river with many things and some have accepted it as their god but after the Muslim’s invasions on the subcontinent, it was called Ja – E – Alam (Place of Knowledge).
Location
The coordinates of the river are29’23’23” in the North while 71’3’42” in the East.
Geography
After originating in Tibet, the water flows through India while forming the Sutlej River which flows through Indian Occupied Kashmir and enters Pakistan. After entering Pakistan it flows through the Kasu and Bhedian districts of Punjab and joins River Indus in Bahawal – Pur.
Furthermore, after joining the Indus River it flows through Karachi, port Bin Qasim and joins the Arabian Sea. The total length of the river is approximately 1450 kilometers.
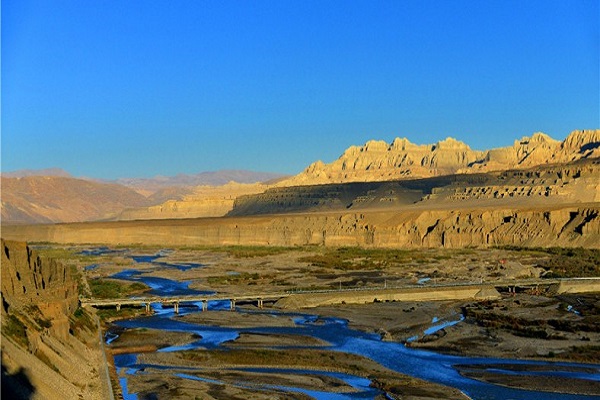

Hydroelectric Power Plants
Many dams and hydroelectric power plants are constructed on the river in the Indian Territory. Bhakra Dam is constructed on the river which has the capacity to produce 1325 megawatts of electricity and considered to be the major hydropower plant of the river.
Furthermore, Karcham Wangtoo Hydr0 – Electric Power Plant is constructed on the river which has the capability to produce 1000 megawatt of electricity. In addition to that, Nathpa Jhakri Dam is also constructed by the Indian government which has the capacity to produce 1200 megawatts of electricity.
A number of other projects are also going on in India under the name of Baspa – II, Bhakra, Sanjay Bhabha, and Nathpa Jhakri.
Tributaries
Rakshastal Lake is considered to be the main tributary of the river which is located in Tibet but due to the tectonic activity, it has been now diverted. Another tributary of the river is the Nascent River which joins the Sutlej River after flowing about 260 kilometers.
Small streams flow from the glaciers of the Himalayas in Tibet, China which contributes to form the river of Sutlej. The river of Sutlej is itself a tributary of the Indus River as after entering Pakistan; it flows through the rivers of Panjnad and Chenab and meets the Indus River at a distance of hundred kilometers from Bahawalpur.
Canals
Many canals are excavated on the river including Sirhind Canal which was opened in 1882. It provides water for irrigation to more than 2 thousand square miles of agricultural land. Furthermore, the canal is used for transporting goods to the other regions of India as the length and width of the canal are considerable for transportation.
Another canal under the name of Sutlej – Yamuna is started constructing in India which will contribute to the trading service of India as it is a short route and save enough time and energy and will be used for traveling service to many destinations.

Sutlej River Dispute
A dispute took place after the independence of Pakistan, on the water of the rivers which flows through India and enters Pakistan. India took advantage of diverting the water of the Sutlej to their territory before Indus Water Treaty.
In 1960, all of the rivers were divided between India and Pakistan under International Water Sharing Treaty. The river of Sutlej was allocated to India along two other rivers but Pakistan was permitted to use Indian rivers till the construction of their own canal system.
Pakistan was allocated the rivers of Chenab and Jhelum which flow through Pakistan and a number of dams and hydroelectric power plants are constructed on it.
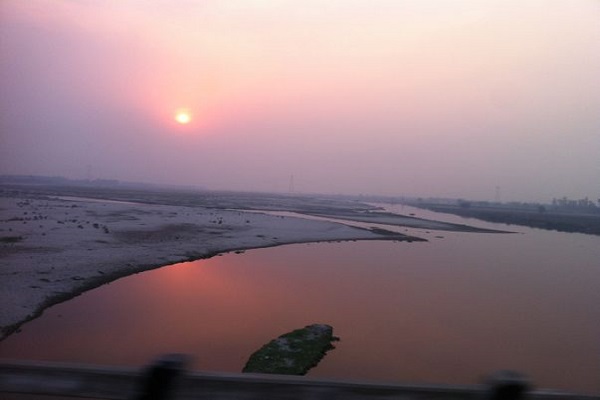

Pollution
The poor sewage system of the nearest villages of the sea, as well as agricultural and industrial wastes, is the main reason for polluting the water of the river. A number of industrial wastes are pushed toward the water of the river which endangers aquatic life as well as makes the water harmful for drinking and irrigating crops.