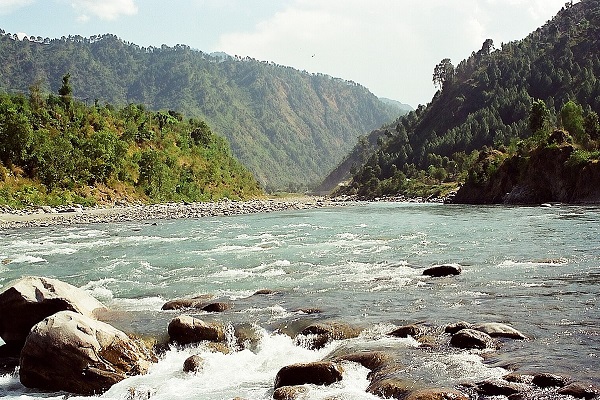
Ravi River is a huge tributary of the Indus River which is formed from the glaciers of Himalayas, India, and flows through the northwest of India in the regions of Chamba and Jammu Kashmir. The water of the river flows at a distance of 80 kilometers (50 miles) and enters the province of Punjab, Pakistan.
In Pakistan, it flows through Kamalia and joins River Chenab at a distance of 725 kilometers from Kamalia, near Ahmadpur. Furthermore, the water of the river is used in both countries Pakistan and India, for drinking as well as irrigation purposes. There are a number of dams constructed on rivers in India while only one canal in Pakistan under the name MRL Canal (Marala – Ravi Link Canal).
The water of the river was a big reason for their disputes which was resolved in 1960 under the Indus Water Treaty, still violated by the government of India by blocking the water of the river. The article comprises all the information about the river Ravi River History.
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Information | |
| Location: | Pakistan |
| Type: | River |
| Local Language Name: | راوی |
| Coordinates : | 30°35?N 71°49?E |
| Location | |
| Countries: | Pakistan and India |
| Provinces: | Punjab |
| Cities: | Lahore |
| Tributaries | |
| Right -: | Siul |
| Source | |
| Location: | Pradesh, India |
| Mouth | |
| Location: | Indus River System |
| Details | |
| Length: | 720 km (450 mi) |
| Discharge average: | 267.5 m3/s (9,450 cu ft/s) (near Mukesar ) |
| Dams: | Chamera Dam, Chamera II Hydroelectric Plant, Ranjit Sagar Dam |
Table of Contents
Ravi River History
The history of the river goes back to ancient times and was known as Iravati or Purushni in Vedas. A battle was fought on the water of the river which is named The Battle of 10 kings, which is mentioned by Nirukta.
Origin
The water of the river originates from the glaciers of the Himalayas Range of Multan in Himachal Pradesh, India. It flows through Bara Banso, Barabhangal followed by the district of Chamba. In Himachal Pradesh, the water flows through Bharmour followed by District Chamba of India and enters Jammu Kashmir while entering Pakistan.
After entering Pakistan, the river flows about eighty kilometers in Pakistani territory and joins River Chenab which is considered to be one of the major tributaries of River Indus.
Tributaries
There are many tributary streams and rivers in India which contribute to form Ravi River. One of the major tributaries of the river is River Budhil in India with a total length of 45 miles. The Budhil River flows through the Himachal region of Bharmour and joins the Ravi River.
Another main tributary is River Nai which originates from the glaciers at the pass of Kali Debi and joins Ravi at Trilokinath. The river of Seul is another major tributary that contributes to the water of the Ravi and joins it near Bharmour.

Contribution
The river is contributing to irrigate a huge area of India where a number of dams are constructed by the Indian government. A number of canals are constructed in India which provides irrigation facilities to the people.
The river’s sewage contributes to the cultivation of different varieties of crops in the Indian Territory. Furthermore, in Jammu Kashmir, the leakage of the river’s water resulted in the greenery of the region.
In Pakistan, a canal under the name of MRL Canal (Marala – Ravi Link Canal) is constructed, through which the water of Chenab River, near Marala Headwork, flows to join River Ravi where the water is distributed to many canals and is used for irrigation purpose.
Hydro-Electric Power Plants
There are a number of Hydroelectric power– plants constructed in India among which some are as follows.
Madhopur Headwork is one of the earliest Head – Work of India, constructed in 1902. It was built on the river in order to divert the water in order to provide the facilities of irrigation.
Baira Suil Hydro – Electric Power Plant is constructed on the river by the government of India in 1980 which has the capacity to produce 198 Megawatts of electricity. Furthermore, the hydropower plant of Chamera – I is installed which has the capacity to produce 540 Megawatts of electricity.
Another power plant is installed under the project of Ranjitsagar Multipurpose Project which has the capacity of producing 600 Megawatts of electricity. In addition to that, a hydroelectric power plant is also installed on the river under the name of Chamera – II which has the capacity to produce 300 megawatts of electricity.

Canals
Most of the canals on the river are situated in India which provides water to the Indian province of Punjab while in Pakistan Marala Ravi Canal is the one that flows from Chenab to Ravi near Sialkot.
MRL Canal was built in 1956 in order to transfer the water of River Chenab to River Ravi and irrigate the land of Gujranwala as well as Sialkot containing 60 thousand hectares approximately.
Disputes
India and Pakistan had a long-termed dispute on the water started in 1947 and ended in 1960. Indian government diverted most of the river’s water and developed the 3 rivers which was given to them in the treaty of 1960.
A treaty was signed on the river’s division between India and Pakistan through which the river of Ravi was allocated to India but permitted Pakistan to use the water of the river till the improvement of the canal system in Pakistan.
Int’l Water Sharing Treaty
Under the World Bank’s treaty of International Water Sharing Treaty of 1960, three rivers were given to India for their usage as they had already developed these rivers before the treaty.
These 3 rivers include Beas, Ravi, and Sutlej which were allocated to India while the remaining rivers including Chenab and Jhelum were allocated to Pakistan for their usage. The treaty is named as international Water Sharing Treaty, but it resulted in the division of the rivers rather than sharing of the water of all rivers to both countries.

Water Pollution
The water of the river is flowing through Indian Punjab where it is polluted through industrial wastes and chemicals as well as home drainage. Other sources of water pollution include agricultural wastewater.
These sources pollute the water of the river and endanger the aquatic life of the river as well as reduce the production of the crops as it is used to irrigate the crops in the Indian province of Punjab. In Pakistan, it is also polluted by the people of Punjab through their homes due to bad sewerage and drainage system.
Social Media Handle
https://www.facebook.com/raviriverproject/